29.1 Principle
Increasing loads are applied in specified steps to a diamond scratching point of defined geometry
The resistance to scratching of the decorative laminate sheet under test is expressed as a numerical rating which defines the maximum applied load which does not produce a continuous surface scratch. The test result is verified by visually confirming that the next higher load-step produces a continuous scratch.
29.2 Materials
29.2.1 Contrast medium, e.g, graphite, talcum, or solution of dye in alcohol, to contrast with the colous of the sheet under test.
29.2.2 Supply of cotton fabric
29.3 Apparatus
29.3.1 Scratch testing apparatus, (see Figure 18), consisting of the following parts:
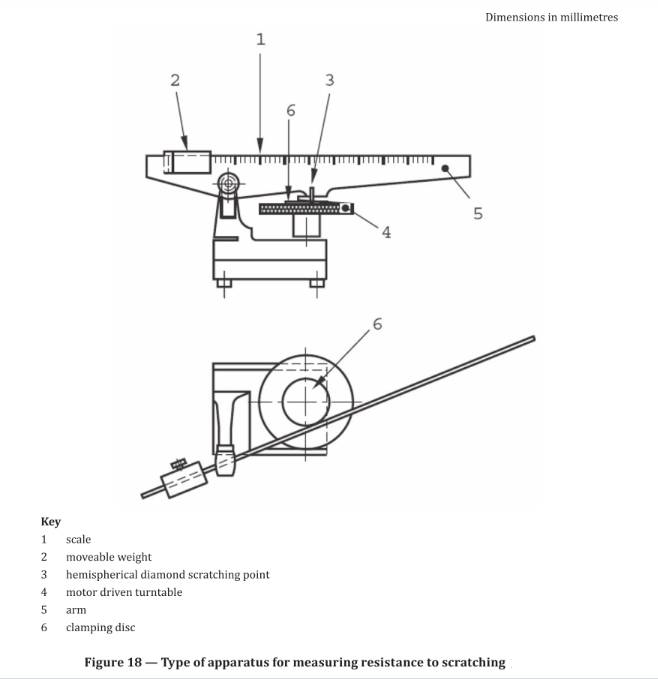
29.3.1.1 Stand, with a device to indicate the horizontal, for example a spirit level
29.3.1.2 Motor driven turntable, able to rotate about a vertical axis without play. The rotational frequency shall be (5 +/- 1) revolutions per minute.
29.3.1.3 Arm, carrying the holder for the diamond, mounted on a ball bearing, with a horizontal axis The height of this axis shall be adjustable so that the arm is exactly horizontal when the scratching point rests on the test specimen
29.3.1.4 Means of applying a known load, with an accuracy of +/- 0.1 N to the scratching point.
29.3.1.5 Hemispherical diamond scratching point, with a point radius of (0,090 ± 0,003) mm and an included angle of (90 ± 1) degree (see Figure 19). (The diamond shall be mounted in the holder with the flat part on the leading side of the shank facing the working direction.)
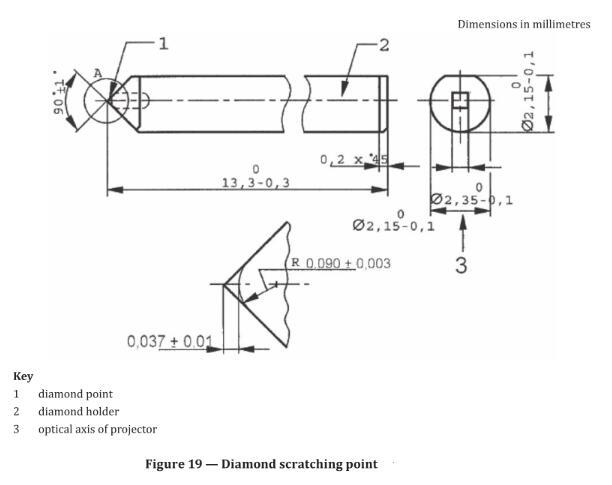
NOTE 1 The crystal axis of the diamond shall be parallel to the longitudinalaisof the diamond holder. The dimensions of the diamond holder are approximate and are for information only.
NOTE 2 Diamond Points conforming with these dimensions and profile are available from: Cie Weinz, Industrie Edelstein Fabrik, Postfach 2740, D-55743 Idar-Oberstein, Germany: and through Erichsen GmbH and Co. KG, D-58675 Hemer-Sundwig/Westfallen, Germany
NOTE 3 This is an example of a suitable product that is available commercially. This information is given for the convenience of users of this part of ISO 4586 and does not constitute and endorsement by ISO of this product.
29.3.1.6 Clamping disc, to keep the test specimen flat
29.3.2 Viewing enclosure, having a matt black interior and a light source (defined below) located at the top. Its dimensions shall be such that the test specimen is located vertically below the light source and at a distance of 600 mm. An aperture in the front shall allow inspection of the test specimen at various angles from a distance of (400 ± 10) mm. A diagram of a suitable enclosure is shown in Figure 20.
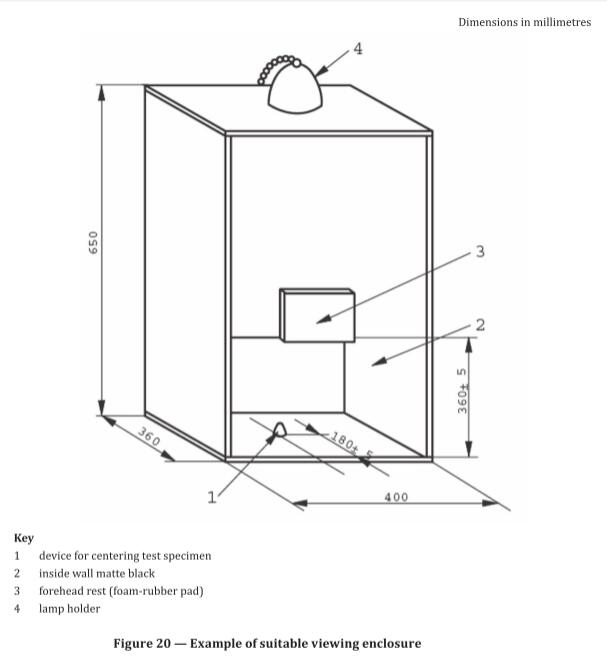
The light source consists of a 100 Watt frosted bulb, mounted in a white reflector having ar aperture of approximately 140 mm diameter and producing an illumination of 800 lx to 1000 lx at the specimen surface.
29.3.3 Conditioning chamber, in accordance with ISO 291, with a standard atmosphere of (23±2) ℃ and relative humidity (50 ± 5) %.
29.4 Calibration of apparatus
Place the diamond point on the table of the electronic balance (see 29.3.4) and, with arm in a horizontal position, verify that the position marks for sliding weight correspond to the load values shown in Table 4. If not, move weight as necessary to achieve the correct loads, and mark the correct positions on arm.
Table 4 ---- Load values
|
Position mark
|
1,0 N
|
2,0 N
|
4,0 N
|
6,0 N
|
|
Load (grams force)
|
102 +/- 1
|
204 +/- 1
|
408 +/- 1
|
612 +/- 1
|
29.5 Test specimen
The test specimen shall be a square of side (100 ± 1) mm cut from the sheet under test.
One specimen shall he tested.
Wipe the specimen sur face using cotton fabric (sse using cotton fabric (see 29.2.2) impregnated witl ed in the test area.
Before making the scratch test, store the specimen for 72 h in the standard atmosphere specified in 29.3.3
29.6 Procedure
Make sure that the stand of the test apparatus is standing horizontally. Adjust the height of the arm so that it is horizontal when the diamond point rests on the test specimen.
Start the test by making two scratches at 1,0 N load with a spacing of 1 mm to 2 mm between the scratch marks.
On the same specimen repeat this procedure with loads of 2,0 N, 4,0 N, and 6,0 N, leaving a space of mm to 5 mm between each pair of scratches.
Remove the specimen from the apparatus and rub the entire scratched area of the surface with a suitable contrast medium (see 29.2.1) so that it is engraind in any scratches.
Carefully wipe the surface with clean cotton fabric (see 29.2.2) to remove any excess contrast medium which is not engrained in a scratch. This procedure is necessary to ensure that only true scratches are considered, and superficial hairline polish marks are ignored
Place the specimen against the centre support in the viewing enclosure (see 29.3.2) in a position so that the specimen can be viewed at right angles to the plane of the surface.
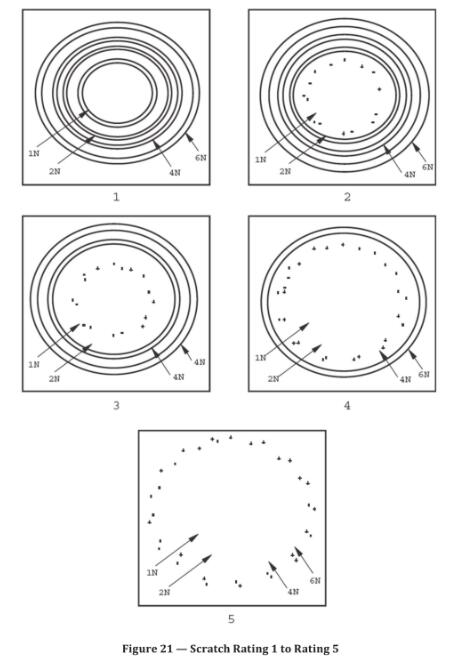
Examine the surface to determine the lowest load for which an almost continuous (ie. > 90 %) double ircle of scratch marks can be seen. The examples shown in Figure 21 can be used as a guide.
A scratch mark is where the contrast medium is engrained in the scratch, and is clearly visible as a line of colour contrasting with the colour of the specimen.
Seperficial polish marks (ie. where there is a change in gloss level but no continuous engrained contrast medium) shall be ignored
The examination of the surface shall take no longer than 10 s, and the operator must ensure that the double circle of scratch marks selected is truly > 90 % continuous.
29.7 Expression of results
The scratch resistance of the laminate under test shall be expressed in accordance with the rating scale hown in
Table 5. See Figure 21 for further explanation:
Table 5 --- Scratch resistance rating scale
|
Discontinuous scratches, or slight surface scratches,
or no visible marks
|
≥90% of continuous double circles clearly visible traces
|
level 5
|
6 N
|
|
level 4
|
4 N
|
6 N
|
level 3
|
2 N
|
4 N
|
level 2
|
1 N
|
2 N
|
level 1
|
--
|
1 N
|
29.8 Test report
The test report shall include the following information: a) a reference to this part of IS0 4586, ie ISO 4568-2015;
b) name, type and nominal thickness of the product;
c) scratch resistance, expressed in accordance with the rating scale
d) any deviation from the specified test method;
e) date of the test.




 ONLINE
ONLINE +86(551)82322038
+86(551)82322038 cfinspection@aliyun.com
cfinspection@aliyun.com